Remote System Access via SSH (Server Setup Focus)
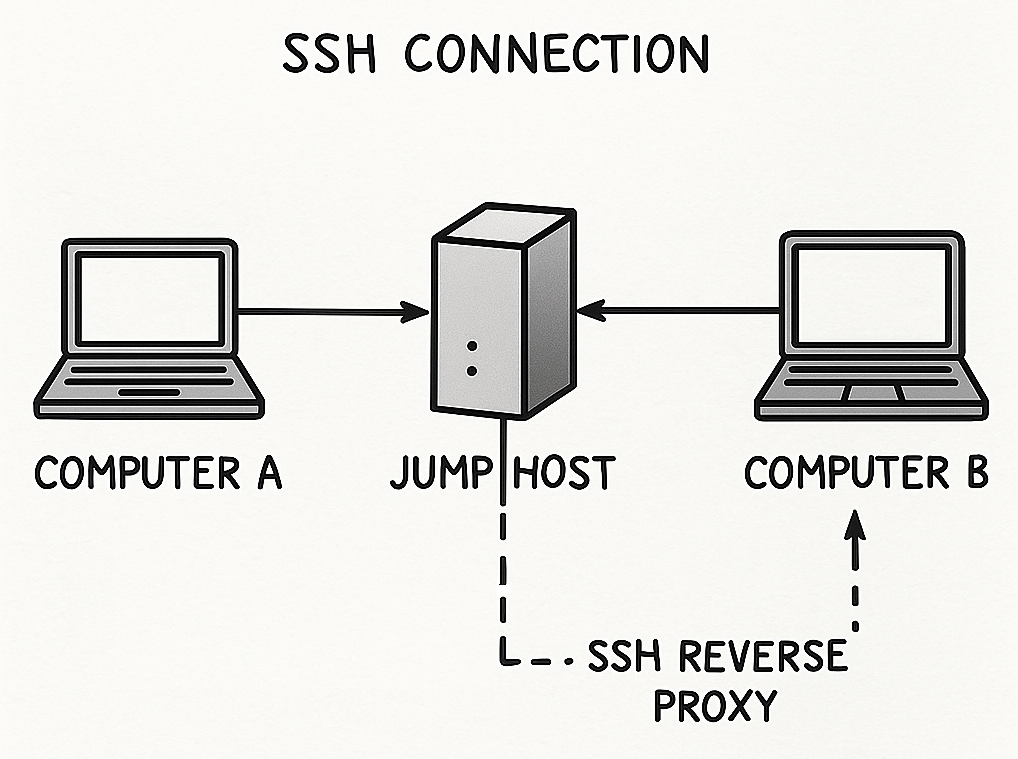
This document details the server-side setup for establishing remote SSH access to a client machine via a jump host, using a reverse SSH proxy.
1. Server Setup: Jump Host Configuration
The jump host acts as an intermediary for establishing the reverse SSH tunnel.
-
Run the
ssh-proxy_serverDocker image. https://github.com/MirAI-Tech-Dev/remote-connect -
Default Username: The image uses a default username for the reverse proxy:
backflip. -
Add Client Key to
authorized_keys: The client’s public SSH key must be added to/home/backflip/.ssh/authorized_keyson the jump host.The
authorized_keysentry should be configured to only allow tunnel setup (specifically on port 2222) and prevent direct command execution or login shells. An example configuration is:command="",restrict,port-forwarding,permitopen="localhost:2222" ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIBcgKNOj/IeWHZ5Q3q87dBiS9EyU70jJi8O8idqoNWhO matthias@my-testYou can add or modify this entry by connecting to the jump host and using
nano:ssh remote-connect-login -l backflip -t -- nano .ssh/authorized_keys
2. Obtain the Public Key from the Client
Instruct the client to provide their public SSH key. They can typically do this using one of the following commands:
- For RSA keys:
cat ${HOME}/.ssh/id_rsa.pub - For ED25519 keys (newer systems):
cat ${HOME}/.ssh/id_ed25519.pub
3. Create SSH Key Pair on Client (if missing)
If the client does not have an SSH key pair, they should generate one using:
ssh-keygen
Important: Advise the client not to enter a password when prompted during key creation.
4. Create a Tunnel from the Client Machine
The client machine will establish a reverse tunnel to the jump host (ssh-proxy_server container). This command opens a tunnel that forwards connections from a specified port on the jump host (R_PORT) to port 22 on the client’s localhost.
SSH_PROXY=SSH_PROXY_IP_OR_NAME
R_PORT=2222
ssh ${SSH_PROXY} -p 11111 -l backflip -R ${R_PORT}:localhost:22 -N -T -v
Optional: Add Jump Host to Client’s ssh_config
To simplify the client-side tunnel command, the client can add the following to their ~/.ssh/config file:
host rev-proxy
ForwardAgent yes
hostname SSH_PROXY_IP_OR_NAME
user backflip
port 11111
With this configuration, the tunnel can be initiated using:
R_PORT=2222
ssh rev-proxy -R ${R_PORT}:localhost:22 -N -T -v
5. Connect to the Client from an Authorized Machine
Once the tunnel is established, an authorized machine can connect to the client. The machine initiating this connection must have its SSH key authorized by the jump host.
JMPBOX=backflip@SSH_PROXY_IP_OR_NAME:11111
USER_CLIENT=andrew
R_PORT=2222
ssh -J ${JMPBOX} -p ${R_PORT} -l ${USER_CLIENT} localhost
Optional: Add Reverse Tunnel Connect to ssh_config
To streamline connections to the client, add the following to the authorized machine’s ~/.ssh/config:
host rev-proxy-connect
ForwardAgent yes
hostname localhost
#user USER_CLIENT
port 2222
ProxyJump rev-proxy
StrictHostKeyChecking accept-new
UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null
After this configuration, connect to the client simply by:
ssh rev-proxy-connect -l USER_CLIENT